In the Driving Seat: Memory Components for Automotive Applications
While the first cars were a marvel of mechanical engineering, the electronics in today’s cars play an equally important role. Largely responsible for control, safety, and convenience, automotive electronics have spurred constant and relentless innovation in the car industry. The list of electronics in vehicles is endless: vehicle navigation systems, communication, infotainment systems, airbags, parking sensors, etc. It is estimated that the average car uses more than 1,000 semiconductor chips. This dependency became apparent during the global chip shortage when car manufacturing experienced unprecedented delays.
Fail-safe
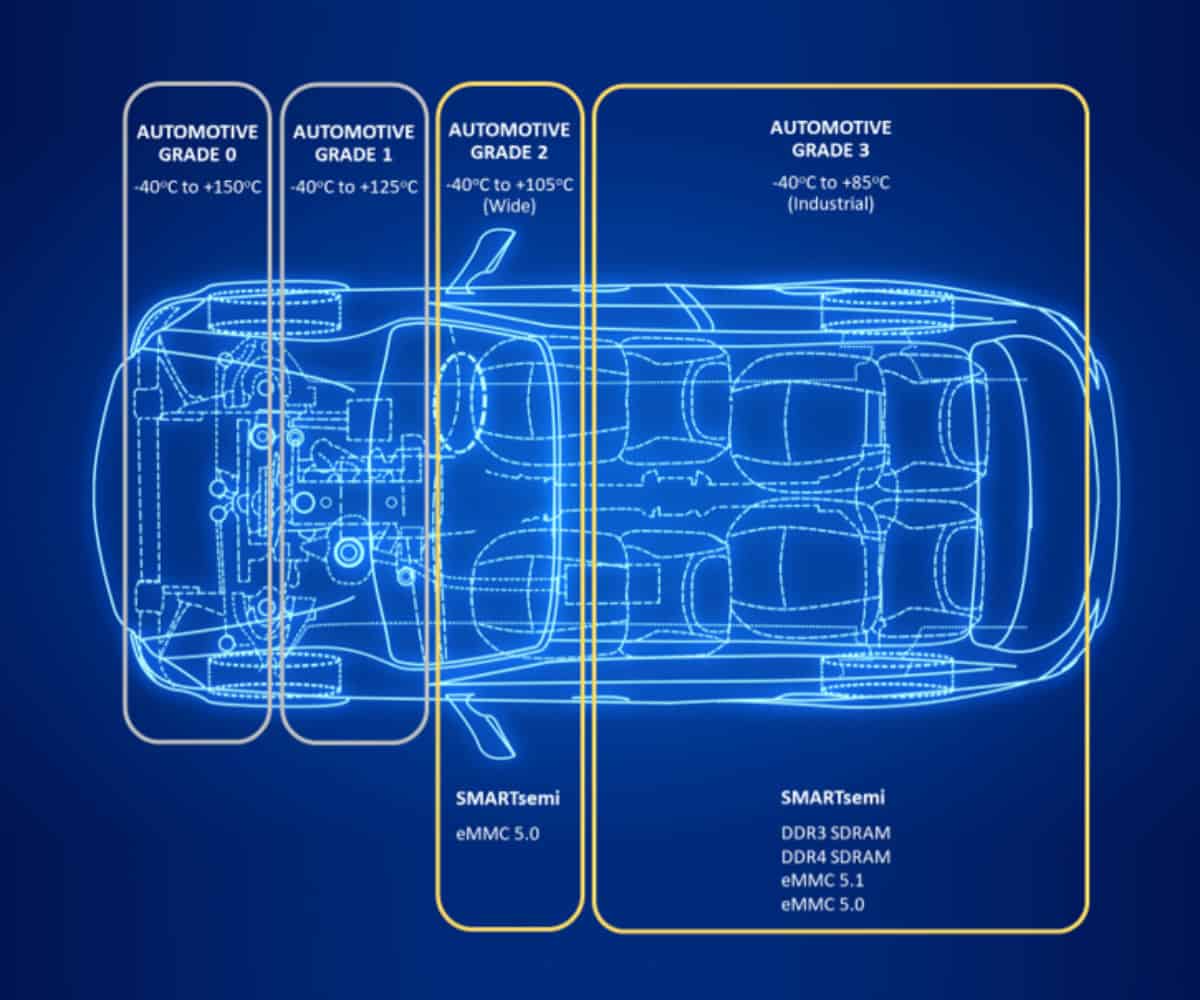
Given how much the vehicle, its driver, the passengers, and the other road users depend on automotive electronics for their safety and control, it is unsurprising that ICs used in automotive applications are subject to high performance, reliability, and endurance standards. Strict regulations are geared towards minimizing failure. If a component or part fails, it needs to do so as safely as possible. The automotive temperature grading system, outlined in AEC-Q100, is used to qualify components based on safe operating temperature for a specific application. For example, Wide-Temperature range components for automotive applications are grade 2. They operate reliably in environments between -40°C and +105°C. Technologies in the interior of cars, like infotainment systems, vehicle navigation systems, and door controls, generally fall within grade 2, while under-hood electronics typically require grade 1 or grade 0 components as they can be subject to an even wider temperature range during operation.
Memory components for automotive applications
When it comes to memory components in automotive applications, vehicles use different kinds of distributed memory, including FLASH, ROM, DRAM, and SRAM. Cars have become increasingly sophisticated and with it also the requirements for the used data storage and memory components. Automotive applications can be quite demanding of the embedded ICs with multiple power up/down cycles per day and operating periods that usually stay under one hour but occasionally reach a multiple thereof. On top of that, in the US, cars are typically in use for 12.2 years meaning the memory components for the automotive industry need to work every day reliably for more than a decade.
A recent example of a recall as a result of worn-out memory chips was in late 2020 when the US National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) found that 8GB eMMC NAND flash devices in over 130,000 Tesla’s were reaching their program/erase (P/E) cycle limit after three to four years. This storage component failure in the central infotainment system caused malfunction of the window demisting system and the rearview camera, as well as potentially affecting the turn signal and Autopilot functionality. For the NHTSA, the failure of the memory component posed a big enough safety risk to advise a full recall.
Ready. Set. Go.
Memory devices for the automotive industry go through careful qualification and testing at each stage of design, production, and integration. The selected components should meet strict requirements in regard to performance, reliability, speed, and endurance. Sourcing from a reliable partner is the first step to a solid supply chain. At SMARTsemi, we understand the challenges of each of the markets that we serve. We recently added automotive grade 2 eMMC 5.0 to our product range and are ready for sample requests.
SMARTsemi is your supply chain partner for DRAM components, eMMC solutions, and SD/microSD Flash Memory Cards for long-life applications. With 20+ years of industry experience, we understand your challenges and have aligned our priorities with yours to simplify your memory chip supply chain for the long run. We know what you need before you need it. Get a jump start and request a sample today.